Robot with a Biological Brain: new research provides insights into how the brain works – University of Reading
14 August 2008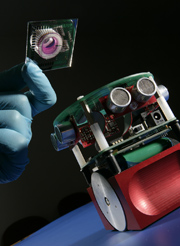 Watch our interview with Professor Kevin Warwick, School of Systems Engineering, and Dr Ben Whalley, School of Pharmacy (WAV - 57MB)
Watch our interview with Professor Kevin Warwick, School of Systems Engineering, and Dr Ben Whalley, School of Pharmacy (WAV - 57MB)
A multidisciplinary team at the University of Reading has developed a robot which is controlled by a biological brain formed from cultured neurons. This cutting edge research is the first step to examine how memories manifest themselves in the brain, and how a brain stores specific pieces of data. The key aim is that eventually this will lead to a better understanding of development and of diseases and disorders which affect the brain such as Alzheimer's Disease, Parkinson's Disease, stroke and brain injury.
The robot's biological brain is made up of cultured neurons which are placed onto a multi electrode array (MEA). The MEA is a dish with approximately 60 electrodes which pick up the electrical signals generated by the cells. This is then used to drive the movement of the robot. Every time the robot nears an object, signals are directed to stimulate the brain by means of the electrodes. In response, the brain's output is used to drive the wheels of the robot, left and right, so that it moves around in an attempt to avoid hitting objects. The robot has no additional control from a human or a computer, its sole means of control is from its own brain.
The researchers are now working towards getting the robot to learn by applying different signals as it moves into predefined positions. It is hoped that as the learning progresses, it will be possible to witness how memories manifest themselves in the brain when the robot revisits familiar territory.
Professor Kevin Warwick from the School of Systems Engineering, said: "This new research is tremendously exciting as firstly the biological brain controls its own moving robot body, and secondly it will enable us to investigate how the brain learns and memorises its experiences. This research will move our understanding forward of how brains work, and could have a profound effect on many areas of science and medicine."
Dr Ben Whalley from the School of Pharmacy, said: "One of the fundamental questions that scientists are facing today is how we link the activity of individual neurons with the complex behaviours that we see in whole organisms. This project gives us a really unique opportunity to look at something which may exhibit complex behaviours, but still remain closely tied to the activity of individual neurons. Hopefully we can use that to go some of the way to answer some of these very fundamental questions. "
ENDS
For more information please contact Dr Lucy Chappell on 0118 378 7391 or 0751 518 8751 or email l.chappell@reading.ac.uk
Notes to editors:
A two page feature about this research appears in New Scientist issue 16/08/08
This project has been funded by the UK Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council.
Dr Ben Whalley is a registered Pharmacist from the School of Pharmacy at the University of Reading. Professor Kevin Warwick is Head of Cybernetics in the School of Systems Engineering at the University of Reading.
The University of Reading is ranked as one of the UK's top research-intensive universities. The quality and diversity of the University's research and teaching is recognised internationally as one of the top 200 universities in the world. The University is home to more than 50 research centres, many of which are recognised as international centres of excellence such as agriculture, biological and physical sciences, European histories and cultures, and meteorology.
The most recent Research Assessment Exercise confirms our strengths, with 20 departments being awarded top ratings of 5 or above. Of these, Archaeology, English, Italian, Meteorology and Psychology each received a 5** rating in recognition of their high quality sustained over more than a decade. The University takes a real-world perspective to its research and is consistently one of the most popular higher education choices in the UK
